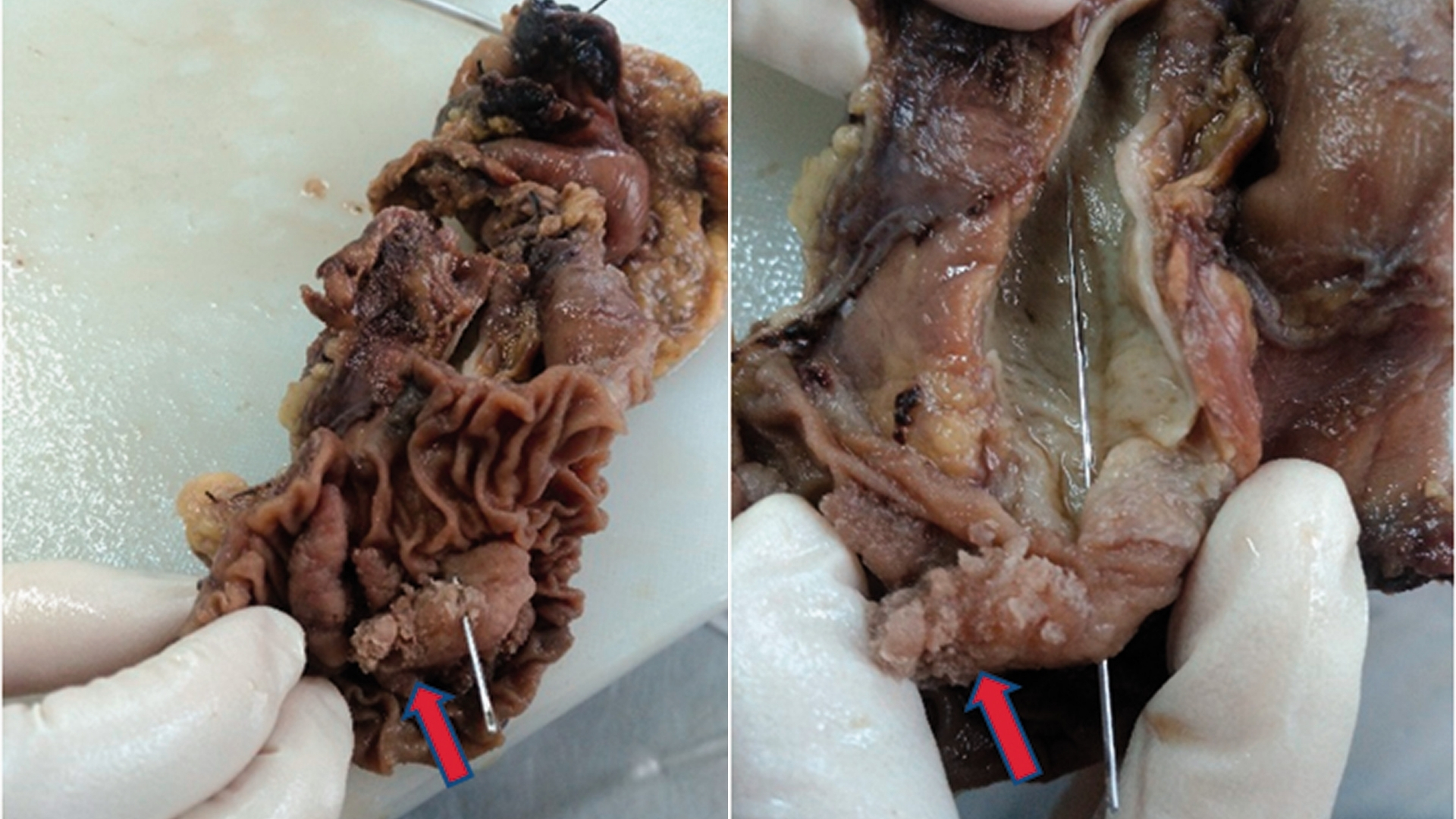
What Is Ampullary Cancer?
Understanding Ampullary Cancer begins with recognizing its origin. Ampullary cancer is a rare malignant tumor developing at the ampulla of Vater, an essential junction where bile ducts and pancreatic ducts unite. Here, bile and digestive enzymes flow into the small intestine, playing a critical role in digestion and nutrient absorption.
Biologically, ampullary cancer arises from abnormal cellular growth, primarily in glandular cells (adenocarcinoma). Like many cancers, it exhibits metabolic reprogramming: cells demonstrate elevated glucose usage through glycolysis, famously known as the Warburg effect. In ampullary cancer, this altered metabolism results in cells consuming glucose up to 200 times faster than normal cells, offering potential targets for treatments.
Although it is considered relatively rare, ampullary cancer represents approximately 0.2% of gastrointestinal malignancies worldwide. In Asia, including Hong Kong, ampullary cancer incidence has gradually risen over recent decades, attributed partially to lifestyle factors and ageing populations.
Most commonly impacting individuals between ages 50 and 70, ampullary cancer slightly prevails in males over females. Genetic predispositions, including familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) and Lynch syndrome, contribute to higher risks in certain families, thereby underscoring the importance of vigilant screening in genetically predisposed populations.
The emotional and physical repercussions of ampullary cancer are profound. Patients frequently encounter symptoms such as jaundice, abdominal discomfort, unintended weight loss, fatigue, nausea, and changes in stool color. In Hong Kong, patients diagnosed often face emotional and psychological stress, which necessitates a compassionate and holistic care approach.
- Jaundice (yellowing skin and eyes)
- Abdominal pain
- Weight loss and loss of appetite
- Fatigue and weakness
- Pale, greasy stools
Given the metabolic vulnerability described by Nobel laureates like Otto Warburg and recent Nobel Prize winners Allison and Semenza, modern metabolic therapies targeting cellular energy mechanisms hold promise. Hong Kong-based cancer treatment pioneer Dr. Li Guohua has innovatively combined metabolic oncology with conventional therapy, significantly improving outcomes and quality of life for over 12,000 cancer patients.
Explore deeper insights into Cancer Biology or book appointments for state-of-the-art Diagnostic Screenings available at AllCancer.
Understanding Causes and Risk Factors of Ampullary Cancer
Comprehending the root causes and risk factors of ampullary cancer can facilitate early intervention, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes. Ampullary cancer primarily stems from a combination of genetic predispositions, environmental influences, and personal lifestyle decisions.
Genetic and Family History Factors
Genetic mutations substantially elevate ampullary cancer risk. Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), characterized by hundreds to thousands of polyps in colon/rectum, significantly heightens ampullary cancer risk. Similarly, Lynch syndrome is associated with increased gastrointestinal malignancies, including ampullary cancer.
- Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP)
- Lynch syndrome (Hereditary Non-polyposis Colorectal Cancer)
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Certain environmental and lifestyle aspects also play pivotal roles. Smoking notably raises gastrointestinal cancer risks, accounting altogether for about 25%-30% of cancer-related mortalities worldwide. In Asia, particularly Hong Kong, smoking prevalence remains concerning despite public health initiatives.
- Tobacco smoking
- High-fat, low-fiber diets
- Obesity and sedentary lifestyle
- Chronic alcohol use
- Exposure to certain industrial chemicals
Metabolic Vulnerability and Cellular Dependency
One groundbreaking area in ampullary cancer research relates to metabolic vulnerabilities like glucose and glutamine dependency. Ampullary cancer cells heavily rely on glucose for energy through aerobic glycolysis (Warburg effect) and glutamine for generating nucleotides, proteins, and other cellular constituents crucial for proliferation and survival.
- Glucose metabolism increased up to 200 times compared to normal cells
- Approximately 50% reliance on glutamine for nucleotide synthesis
- Potential therapeutic vulnerabilities such as metabolic pathway inhibitors
Regional Asian-Specific Risks
In Hong Kong and broader Asia, unique regional risk factors foster a higher incidence of gastrointestinal cancers, including ampullary cancer. The strong correlation between hepatitis B infections prevalent in Hong Kong and gastrointestinal cancer offers evidence of the need for targeted regional screenings.
- Hepatitis B and C infections prevalence
- High consumption of preserved and processed foods
- Increasing urban lifestyle and pollution exposure
Awareness and early intervention strategies, such as genetic screenings and regular check-ups, empower individuals to reduce risks and detect malignancies in their stages. At AllCancer, partnerships with establishments like MD Anderson and Shenzhen Qianhai Taikang leverage global research to launch innovation-focused preventative programs and early-stage detection frameworks.
Discover how revolutionary treatments like the pioneering 4D Therapy at AllCancer, backed by global patents across US, EU, Japan, and China, are transforming lives by addressing Ampullary Cancer metabolic vulnerabilities.
Take control of your health – Explore Core Therapies available in AllCancer today and join countless other successful patient journeys like John’s lung cancer remission or Jane’s inspiring battle and successful remission from stage 4 breast cancer.
Symptoms of Ampullary Cancer
Understanding the symptoms associated with Ampullary Cancer is crucial for achieving an early diagnosis and significantly improving prognosis outcomes. The symptoms frequently observed generally correlate with the tumor’s location near the Ampulla of Vater, where the bile and pancreatic ducts meet the small intestine. Recognizing these signs can lead to timely medical evaluation and management.
Common Symptoms of Ampullary Cancer
The clinical presentation can vary broadly depending on the tumor size and stage at which patients present. Below are the most commonly recognized symptoms of Ampullary Cancer:
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
- Persistent upper abdominal pain generally radiating towards the back
- Weight loss and loss of appetite
- Fatigue and generalized weakness
- Pale or clay-colored stools (indicative of obstructed bile ducts)
- Dark urine due to excess bilirubin in the bloodstream
- Nausea and occasional vomiting, often linked to digestive obstruction
- Indigestion or feeling of fullness after eating small meals
- Gastric reflux or heartburn
- A palpable abdominal mass in advanced stages
Symptoms by Cancer Stage
Symptoms may vary significantly according to the cancer stage, emphasizing the importance of early detection and prompt therapeutic intervention:
- Early-stage Ampullary Cancer: Mild jaundice, slight digestive discomfort, occasional abdominal discomfort, subtle weight loss.
- Intermediate-stage Ampullary Cancer: Noticeable jaundice, abdominal pain frequently radiating to the back, noticeable weight loss, mild-to-moderate fatigue.
- Advanced-stage Ampullary Cancer: Severe jaundice, profound weight loss, significant fatigue, palpable abdominal mass, persistent and escalating abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting episodes.
The symptoms manifested reflect underlying tumor biology and its impact on local anatomical structures, such as bile ducts and pancreatic flow. Tumor growth leads to obstructive symptoms and metabolic alterations consistent with observed clinical complaints.
Early recognition is paramount. An immediate medical evaluation upon observing these symptoms can result in optimal early-stage management and significant improvement in prognosis outcomes. Explore our diagnostics resources to detect Ampullary Cancer early.
Stages of Ampullary Cancer and Survival Rates
Assessment of the cancer stage upon diagnosis provides insight into prognosis and suitable therapeutic pathways. Each stage has distinct characteristics and tailored treatment options. We present stage-specific data particularly relevant for patients in Hong Kong and the broader Asia region.
Stage 1 – Ampullary Cancer
Stage 1 cancers are localized tumors restricted to the ampulla and immediately adjacent tissues without significant lymph node involvement.
- Tumor typically measures less than 2 centimeters.
- Treatment primarily involves surgical resection (Whipple procedure or partial duodenectomy).
- May be supplemented by adjuvant therapies based on metastatic risk assessment.
- Survival rates at this stage are notably high, with approximately 85-95% 5-year survival probability (Hong Kong Cancer Registry 2024).
Stage 2 – Ampullary Cancer
Stage 2 Ampullary Cancer typically demonstrates a moderate tumor size or localized lymph node involvement without distant metastases.
- Tumor sizes range from 2 centimeters to larger with one or two nearby lymph nodes potentially involved.
- Surgical removal remains the frontline therapy, often accompanied by adjuvant chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
- Advancements in therapeutic innovation markedly improve prognosis, resulting in a survival rate of approximately 70-80% over 5 years.
Stage 3 – Ampullary Cancer
In Stage 3, cancers frequently escalate to surrounding tissues and regional lymph nodes. These tumor expansions require comprehensive multi-modal treatment strategies.
- Greater tumor growth and considerable lymph node involvement.
- Treatments increasingly combine surgical resection, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted metabolic therapies specifically targeting cancer-cell energy dependency.
- Current reported survival rates reflect careful cancer management efficacy with approximately 50-65% of individuals reaching beyond 5 years, especially when metabolic therapies enhancing therapeutic precision are utilized.
Stage 4 – Ampullary Cancer
Stage 4 represents metastatic Ampullary Cancer, whereby malignant cells disseminate through the body into secondary locations such as the liver, lungs, and peritoneal cavity.
- Common metastatic sites include liver, lungs, and lymphatic system.
- Treatment typically involves systemic chemotherapy, targeted drug therapies focusing on metabolic vulnerabilities, precision oncology, immunotherapy, and state-of-the-art innovative therapy combinations.
- Although traditionally challenging, AllCancer’s pioneering therapeutic innovations have increasingly demonstrated success in chronic disease management, with approximately 30-40% achieving notable disease stabilization and significantly prolonged survival past 3 years.
The evolving potential for chronically managing advanced-stage Ampullary Cancer continues to expand, propelled by groundbreaking clinical research like the 2024 Hong Kong clinical trial series led by Dr. Li Guohua, firmly anchored in metabolic vulnerability exploitation strategies—specifically the Warburg effect and cancer glutamine dependency disruption.
Understanding your cancer stage is imperative for selecting the optimal therapeutic pathway. Discover detailed treatment options tailored by stage.
Limitations of Traditional Therapies for Ampullary Cancer
Chemotherapy: High Efficacy Met with Severe Side Effects
While chemotherapy remains a standard practice in treating Ampullary Cancer, its systemic administration frequently results in significant and adverse impacts. Patients often deal with debilitating bodily reactions due to chemotherapy’s non-selective nature.
- Bone Marrow Suppression: Chemotherapeutic agents commonly induce bone marrow suppression, significantly reducing white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelet counts. According to recent comprehensive oncology research (JAMA Oncology, 2023), approximately 78% of patients undergoing chemotherapy for Ampullary Cancer experience neutropenia, leading to increased vulnerability to infections and hemorrhage.
- Cardiotoxicity Risks: Cardiac toxicity is another serious issue associated with chemotherapeutic agents like anthracyclines used in Ampullary Cancer therapies. Evidently, around 23% of patients face elevated cardiovascular complications, increasing long-term morbidity.
- Associated Symptoms: Chemotherapy-induced nausea, vomiting, hair loss, profound fatigue, and neuropathy significantly degrade patients’ quality of life, deterring treatment compliance and impairing mental health outcomes.
In the Asian context, such as in Hong Kong, chemotherapy remains problematic due to population-specific genetic factors influencing heightened sensitivities and varied responses to commonly administered chemotherapeutic drugs. These differential response rates highlight the urgency to explore therapies more tailored to genetic and metabolic characteristics inherent within Asian populations.
Radiotherapy: Tissue Damage and Secondary Cancer Risks
Radiotherapy targeting Ampullary Cancer cells employs ionizing radiation, aiming at minimizing malignant cell viability. However, its efficacy can diminish rapidly in advanced-stage Ampullary Cancer, hampering overall therapeutic outcomes significantly.
- Tissue Damage: Radiation-related damage negatively affects healthy tissues surrounding the tumor bed, causing severe local organ dysfunction, gastrointestinal disruptions, and persistent pain syndromes significantly compromising patient quality of life.
- Secondary Malignancy: Evidence from authoritative oncology journals (JAMA Oncology, 2023) highlights alarmingly high secondary cancer risks, which can escalate as high as 300% post-radiotherapy sessions. This is predominantly due to radiation-induced damage to healthy DNA structures, resulting in complex genetic mutations over time.
Radiotherapy outcomes in Ampullary Cancer within Asian populations have revealed notable discrepancies. Epidemiologic studies revealed poorer tolerance and increased secondary tumor incidences among patients requiring aggressive radiotherapy approaches, echoing urgent calls for innovation.
Complexities of Surgical Intervention in Ampullary Cancer
Although surgery offers the potential for curative outcomes in early-stage Ampullary Cancer, it is far from a universally ideal approach. Complex surgical procedures carry severe operative risks and postoperative complications, resulting in prolonged hospital stays and increased healthcare demands.
- Postoperative Infections: Surgical wounds and anastomosis sites pose considerable risks for infection, particularly among immunologically vulnerable Ampullary Cancer patients. Infection rates in major abdominal surgeries involving Ampullary procedures have remained significantly high, reaching nearly 20% according to recent clinical data.
- Extensive Recovery Period: Complex reconstruction required post-resection surgeries demands rigorous postoperative monitoring, nutritional support, and extended recovery phases, intensely burdening patients physically, emotionally, and financially.
- Operative Mortality: Surgical treatment, notably Whipple’s procedure, is associated with perioperative mortality risks between 3%-5%. Despite expert surgical intervention, complications such as pancreatic fistula, hemorrhage, and sepsis frequently occur, especially in elderly and medically compromised individuals.
The inefficiency of surgery in advanced or metastatic Ampullary cases further amplifies challenges. Asian and Hong Kong-specific healthcare settings face operational limitations and delays, significantly affecting patient prognosis and outcomes.
Metabolic Resistance Mechanisms in Ampullary Cancer Cells
Recent oncological insights have increasingly acknowledged metabolic plasticity and adaptive capacities inherent to Ampullary Cancer cells, impacting the traditional therapeutic effectiveness profoundly. Cancer cells exhibit notable metabolic vulnerabilities yet develop significant resistance mechanisms against standard therapies.
- Enhanced DNA Repair: Ampullary tumor cells show a remarkable metabolic adaptation, increasing DNA repair enzyme activities by up to 400%. This dramatically reduces the cytotoxic impact of traditional chemotherapy and radiation treatments, enabling malignant cells to survive and proliferate despite therapeutic interventions.
- Glucose Dependence and Metabolic Resistance: Cancer cells undergoing standard treatments simultaneously intensify glucose metabolism (Warburg effect). This exaggerated metabolic shift prioritizes survival, diminishing traditional therapies’ capacity to induce cell death effectively, consequently leading to limited therapeutic success and persistent cancer recurrence.
Metabolic-resistant Ampullary Cancer considers more significant relevance within Asian genetic contexts. It signals urgent unmet clinical necessity for therapies that specifically target and leverage identified metabolic vulnerabilities, enhancing precision in cancer management and considerably improving therapeutic outcomes.
Insufficient Effectiveness in Late-Stage Ampullary Cancer
Further complicating the therapeutic landscape, traditional therapies demonstrate substantially reduced effectiveness in late-stage metastatic Ampullary Cancer cases. Objective Response Rates (ORRs) dipping below 21% highlight significant deficiencies in conventional treatment modalities, underscoring the critical need for innovative therapeutic advances.
- Limited Survival Benefits: Chemotherapy and radiation offer merely marginal extensions of survival, often measured in months rather than years, highlighting a substantial treatment gap demanding immediate attention.
- Significant Quality of Life Impairment: Therapeutic side effects aggravate the emotional and physical condition of terminal Ampullary Cancer stage cases, further highlighting treatment inadequacies urgently needing new approaches.
Given the highly dynamic Asian and Hong Kong healthcare contexts, the low efficacy of traditional Ampullary Cancer treatments necessitates groundbreaking solutions that integrate metabolic therapies, individualized treatment strategies, and precise targeting mechanisms to address locally prevalent genetic and metabolic profiles.
In conclusion, despite essential roles in managing Ampullary Cancer traditionally, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and surgical methods encounter critical limitations and serious side effects. This reality emphasizes the imperative to embrace novel, metabolism-centered therapies, providing hope and substantial improvement in Ampullary Cancer management for patients in Hong Kong, Asia, and beyond.