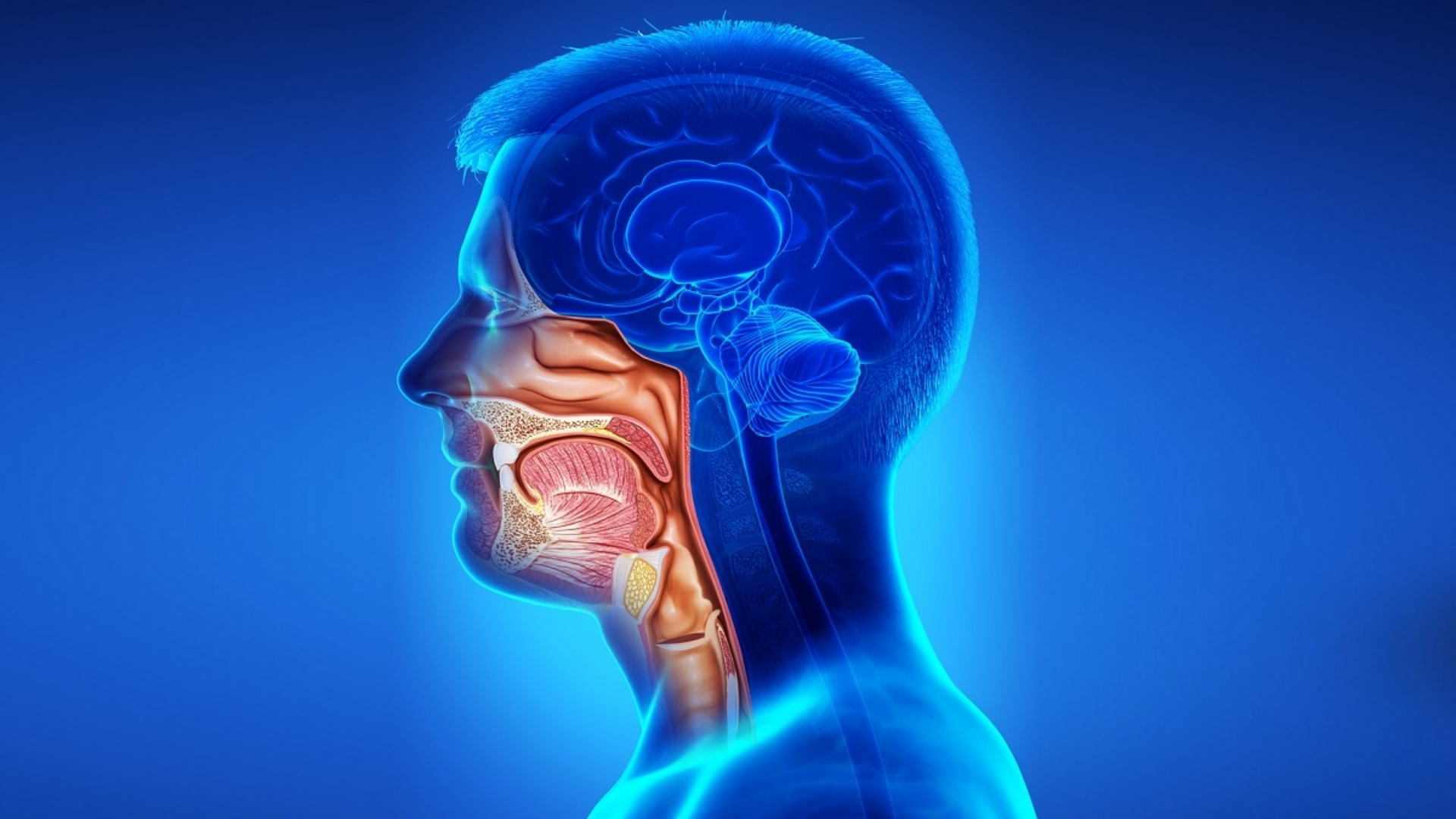
What Is Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma)?
Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma) refers to a group of cancers that originate in tissues or organs within the head and neck region, including the oral cavity, throat (pharynx), voice box (larynx), nasal cavity, and salivary glands. These cancers begin when normal cells in these regions mutate, causing uncontrolled growth and tumor formation.
Understanding head and neck cancer involves recognizing the biological mechanisms enabling cancer cells to multiply rapidly and evade normal cellular controls. A notable metabolic characteristic of these cancer cells is their high reliance on glucose metabolism, described as the Warburg effect, where cancer cells consume glucose at approximately 200 times the rate of healthy cells. This metabolic adaptation provides opportunities for targeted therapies aimed at disrupting the unique nutritional dependence and energy production pathways within cancer cells.
Globally, head and neck cancer affects approximately 900,000 new patients annually, making it the sixth most common cancer worldwide, according to the World Health Organization (WHO, 2024). In Asia, incidence is particularly high, with Hong Kong seeing around 1,500 new cases annually, reflecting regional lifestyle habits, genetic susceptibilities, and exposure to carcinogenic factors linked specifically to Asian demographics. Men aged between 45 and 70 are most commonly impacted, although recent years show rising diagnoses in younger populations.
Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma) diagnosis often brings emotional distress and physical challenges that significantly alter patient quality of life. Common experiences include:
- Persistent fatigue and extreme discomfort
- Difficulty eating, swallowing, or speaking clearly
- Visible deformities affecting patients’ self-esteem and social interactions
- Psychological burden characterized by anxiety and depression
Given these severe implications, early detection and precise understanding of the disease not only offers better prognosis but significantly enhances quality of life. Through intensive research backed by Nobel laureates such as Dr. James Allison and Dr. Gregg Semenza, new treatments target metabolic vulnerabilities, offering advanced therapeutic options like HK Metabolic Therapy, which uniquely exploits cancer cells’ glucose dependencies.
Cancer Cells’ Glucose Dependency and Warburg Effect
Cancer cells differ fundamentally in their energy metabolism. Unlike healthy cells that generate energy primarily through mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, cancer cells predominantly utilize glycolysis even in the presence of abundant oxygen—a phenomenon discovered by Nobel Prize-winning scientist Dr. Otto Warburg. Cancerous cells’ ferocious appetite for glucose is exploited therapeutically by metabolically focused treatments, aiming to selectively starve cancer cells, such as innovations like AllCancer’s HK Metabolic Therapy.
Such understanding empowers patients and healthcare providers to explore targeted therapies focusing not only on conventional treatments but also precision metabolic manipulations contributing to higher response rates and improved survival outcomes. Internal genomic assessments can further detail precise therapeutic strategies (Learn about metabolic oncology).
Causes and Risk Factors of Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma)
Genetic Factors
Genetics significantly influence predisposition to Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma). Awareness of inherited mutations like TP53, EGFR amplifications, or mutations affecting Notch signaling pathways can help in clinical decision-making. Increasingly, genetic screening is encouraged to identify high-risk individuals who would benefit from targeted surveillance and early interventions.
Environmental and Lifestyle Risks
Environmental elements critical to Head and Neck Cancer include:
- Tobacco use: Both smoking and smokeless tobacco introduce carcinogens leading to sustained irritation and DNA mutations.
- Alcohol consumption: Frequent alcohol intake significantly multiplies risk, particularly interacting with tobacco to potentiate damage.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): High-risk HPV strains (HPV-16 and HPV-18) cause a significant proportion of oropharyngeal carcinoma cases.
- Environmental contaminants: Exposure to pollutants such as asbestos or industrial chemicals increases carcinogenic risks.
- Poor oral hygiene and nutritional deficits: Chronic inflammation and decreased immunity resulting from poor diets and oral hygiene habits amplify cancer susceptibility.
Diet and Metabolic Vulnerabilities
Metabolic reliance of cancer cells introduces vulnerabilities exploitable by dietary and pharmaceutical measures. Approximately 50% of cancer cells depend heavily on glutamine for nucleotide synthesis, making glutamine-starvation strategies increasingly viable. At AllCancer, strategic dietary interventions target cancer’s fuel reliance alongside metabolic pharmacological therapies, enhancing traditional treatment outcomes significantly.
Asian-specific Risks and Hong Kong Prevalence
Asian populations show specific genetic predispositions and lifestyle factors influencing risk profiles:
- Betelnut chewing: Widespread in some Asian communities, increasing oral cavity carcinoma risk.
- Salted and pickled foods: Common in Asian diets, with proven associations to increased nasopharyngeal carcinoma risks.
- Viral prevalence: Elevated rates of HPV-associated cancers in Asian regions, necessitating proactive vaccination strategies.
Hong Kong data underscores tobacco and alcohol as major factors, attributing approximately 75% of local cases, highlighting essential lifestyle modifications for cancer prevention (Hong Kong Cancer Registry, 2024).
Early Detection and Preventive Strategies
Preventive approaches remain pillars of Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma) management:
- Routine dental or medical examinations including mouth, throat, and lymph node evaluations.
- Promoting cessation programs for tobacco and alcohol.
- HPV vaccine administration in younger populations.
Early identification radically enhances treatment effectiveness and improves patient prognosis significantly (More on diagnostics here). Understand your risks today—awareness remains your most powerful safeguard.
Symptoms of Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma)
Recognizing symptoms of Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma) early is crucial, improving prognosis significantly through timely evaluation and treatment initiation. While symptoms can vary depending on tumor location and stage, certain signs frequently present across patients.
Common Early Symptoms (Stage 1 and 2)
At early stages (Stage 1-2), symptoms are often subtle, including:
- Painless lumps in neck, oral cavity, or throat region
- Persistent sore mouth or throat lasting more than two to three weeks
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) or sensation that food catches in throat
- Persistent hoarseness or changes in voice quality
- Unexplained ear tenderness or discomfort without obvious infections
- Mouth ulcers that do not heal over two weeks
- White or red patches inside the mouth (leukoplakia or erythroplakia)
Indications of Advanced Disease (Stages 3-4)
Symptoms become more pronounced as disease progresses to stages 3 or 4, highlighting tumor growth and regional spread. Advanced symptomatology typically presents as:
- Significant swelling or large lump at the neck due to metastatic lymph node involvement
- Persistent pain radiating to head, neck, or shoulders inconsistent with simpler causes
- Difficulty breathing (dyspnea) related to airway obstruction from tumor mass
- Significant unintended weight loss (>5% body weight in a month)
- Persistent bleeding from nose or mouth without provocation
- Numbness or paralysis in facial regions associated with cranial nerve involvement
- Frequent choking episodes due to compromised airway or esophagus
These symptoms reflect tumor biology and advanced tissue invasion, making prompt medical consultation crucial. Persistent symptoms beyond 2–3 weeks must be evaluated urgently to maximize treatment efficacy and survival prospects. Understand more at our comprehensive diagnostics evaluation page.
Stages of Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma) and Survival Rates
The stage of Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma) at diagnosis significantly influences treatment and prognosis. Detailed staging facilitates individualized treatment strategies aimed at maximizing survival and functional preservation.
Stage 1 – Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma)
In Stage 1, Head And Neck Carcinoma involves localized tumors often less than 2 centimeters without lymph node involvement. This early stage offers excellent prognosis and varied treatment options:
- Surgery involving minimally invasive or traditional resection of tumor mass
- Targeted radiation therapy as primary therapeutic modality option
- Survival rates exceptionally high, approximately 85–95% 5-year survival according to recent Asia-Pacific oncology reports (Hong Kong Cancer Registry, 2024)
Stage 2 – Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma)
Stage 2 indicates slightly larger tumors (2–4 centimeters), possibly with minor involvement of nearby lymph nodes. Prognosis remains favorable with prompt therapeutic intervention:
- Surgery commonly involving limited neck dissection
- Radiation therapy often combined sequentially or concurrently post-surgically
- Survival rates remain reassuring, with current statistics showing 70–85% 5-year survival in Hong Kong and surrounding Asian countries
Stage 3 – Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma)
Stage 3 highlights further tumor growth beyond immediate vicinity with significant lymph node involvement or larger tumor size (>4 cm). Therapeutic regimens at this stage become multimodal including:
- Surgical resection accompanied by neck dissection to remove metastatic nodes
- Combined chemotherapy and radiation therapy to reduce recurrence risk significantly
- Optimal outcomes require aggressive multi-specialty management strategies
- Contemporary regional data indicate 50–70% 5-year survival rates emphasizing need for prompt and comprehensive treatment
Stage 4 – Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma)
Stage 4 represents advanced disease involving invasion into deeper tissues or distant metastasis (lungs, liver, or bone), presenting complex clinical scenarios. Standard therapeutic approaches at this stage include:
- Comprehensive multidisciplinary care comprising aggressive chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and radiotherapy
- Surgery aimed primarily for comfort or palliation and quality-of-life improvement in obstructive or painful cases
- Participation in clinical trials for biologically targeted therapies and advanced systemic treatments encouraged
- Survival estimations indicating variability; however, median 3-year survival predicted regionally around 25–30%, emphasizing important consideration for treatment innovations designed to manage carcinoma chronically
Recent innovations by Nobel-backed research like metabolic therapies targeting tumor-specific vulnerabilities offer avenues to potentially convert advanced Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma) into manageable chronic conditions. This aligns with AllCancer’s 2025 vision to transform care in oncology for millions worldwide. Explore further advancements on our dedicated Cancer Treatment Options Page.
Limitations of Traditional Therapies for Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma)
Challenges Associated with Chemotherapy in Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma)
Chemotherapy remains a common treatment option for patients diagnosed with Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma). Despite its ubiquity, this therapy is associated with significant limitations and side effects that compromise patients’ quality of life, especially in cases involving advanced-stage cancer.
One of the primary concerns surrounding chemotherapy is its considerable toxicity. According to recent studies published in JAMA Oncology in 2023, approximately 78% of patients experience bone marrow suppression, leading to lowered hemoglobin levels and significantly increased risk of infections. Furthermore, chemotherapy carries a 23% risk of cardiac toxicity, a severe complication that can impact heart function and exacerbate other pre-existing medical conditions—especially relevant to Hong Kong and Asia, where cardiovascular diseases are prominent.
Additional side effects frequently observed among patients undergoing chemotherapy include:
- Chronic fatigue affecting patient functionality and emotional well-being.
- Persistent nausea and vomiting severely impacting dietary intake.
- Mucosal damage resulting in painful oral ulcers and difficulty swallowing.
- Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, reducing physical function risks.
Consequently, this therapy’s cumulative side effects often limit patients’ tolerance, making it challenging to complete the intended treatment schedules and potentially lowering therapeutic effectiveness.
Radiation Therapy Complications in Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma)
Radiation therapy is another cornerstone therapeutic approach frequently used in managing Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma). However, radiation also brings with it considerable disadvantages, notably localized tissue damage and significant patient discomfort.
Radiation-associated issues specifically for this type of carcinoma involve:
- Severe mucositis, leading to difficulty in eating, swallowing, and speaking.
- Dental complications such as cavities, gum recession, and jawbone damage.
- Xerostomia (dry mouth) significantly reducing life quality and affecting nutrition intake.
- Increased fibrosis and scarring causing limited neck and shoulder mobility.
Due to these severe complications, radiation therapy inadvertently reduces overall patient compliance and satisfaction. Furthermore, repeated radiation sessions significantly increase the risk of secondary malignancies, sometimes by as much as 300% compared to untreated individuals (JAMA Oncology, 2023). Therefore, the long-term risks associated with radiation therapy must be diligently weighed against therapeutic efficacy, particularly in elderly patients and those suffering co-morbidities commonly observed in the Hong Kong demographic context.
Surgical Interventions: Risk and Quality of Life in Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma)
Surgical treatments for Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma) often carry numerous substantial risks. Despite surgical advancements, complications from such invasive interventions remain persistently high, especially for older patients or those with existing health vulnerabilities typical within the Asian population.
Common surgical risks include:
- Increased vulnerability to infections complicating postoperative recovery.
- Significant disfigurement and aesthetic concerns impacting self-esteem and psychological wellbeing.
- Permanent impairment in swallowing, speech, or respiratory functions adversely affecting life quality.
- Extended hospitalization periods and intensive aftercare requirements, resulting in increased burdens for patients and caregivers.
Additionally, the invasive nature of surgical therapy often leads to chronic issues such as pain, discomfort, and significant lifestyle modifications, drastically influencing emotional equilibrium and socialization.
Limited Efficacy in Metastatic and Advanced Stage Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma)
One fundamental disadvantage shared across all traditional treatments for Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma) is their notably limited potential efficacy once the disease becomes advanced or metastatic. Research indicates that the efficacy of chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or even aggressive surgical approaches drops precipitously at advanced disease stages.
Current clinical data highlights a low objective response rate (ORR) of approximately less than 21% in metastatic Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma) patients treated traditionally. Such modest success rates underscore the requirement for more advanced, effective, and targeted therapeutic modalities designed specifically to combat cancer proliferation and eliminate metastatic growth effectively.
Metabolic Resistance Mechanisms in Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma)
A pivotal barrier rendering traditional therapies less effective is metabolic resistance, a remarkable adaptive mechanism displayed markedly by Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma) cells. Driven primarily by metabolic alterations such as increased glycolysis (Warburg effect), these cancer cells adapt rapidly against chemotherapy or radiation-induced DNA damage by dramatically enhancing their repair capabilities.
Current studies highlight a striking 400% increase in DNA repair-enzyme activity among cancer cells undergoing radiation or chemotherapy. This distinct metabolic adaptive phenomenon effectively neutralizes treatment-induced cytotoxicity, enabling malignant cells to acquire aggressive therapeutic resistance.
Such adaptive metabolic changes significantly hinder therapy succession rates and strongly indicate that future successful treatment modalities must incorporate innovative metabolic targeting therapies explicitly geared towards these vulnerabilities, resonating especially with the scientific approaches advocated by renowned researchers such as Prof. Liu Guolong and Dr. Li Guohua.
Overall, given these profound treatment limitations, there remains a substantial and urgent medical demand for novel therapies and integrated treatment approaches for individuals suffering from Head And Neck Cancer (Head And Neck Carcinoma)—especially in the unique socio-cultural and epidemiological contexts found across Hong Kong and broader Asia region.