Understanding Sézary Syndrome (Leukemic Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma)
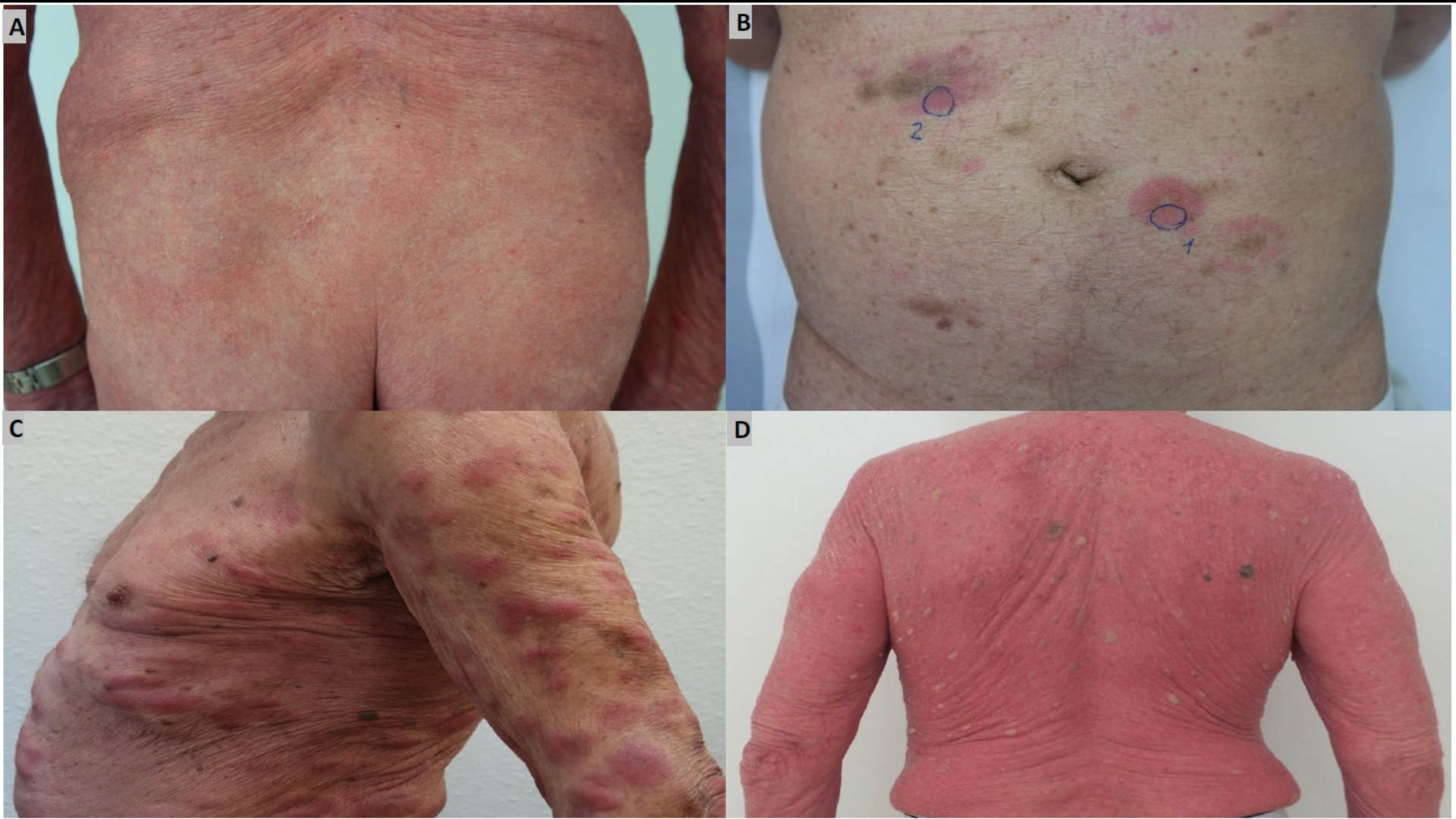
Sézary syndrome (Leukemic Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma) represents a rare, aggressive type of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma characterized by the presence of cancerous T-cells in the skin, lymph nodes, and blood. These cancerous cells exhibit metabolic adaptations such as the Warburg effect, where they consume glucose at rates 200 times higher than normal cells, fueling rapid growth and proliferation. The syndrome is more prevalent in older adults, generally affecting individuals over the age of 60, with a slightly higher incidence in males. Although relatively rare, it causes a significant physical and emotional burden, manifesting symptoms such as intense itching, skin lesions, fatigue, and potential systemic complications.
In Hong Kong and other parts of Asia, understanding Sézary syndrome’s impact is crucial given the rising incidence of autoimmune and immune-related disorders. The psychological burden of living with a chronic condition like this cannot be understated, as patients grapple with physical discomfort alongside the anxiety and depression that may accompany prolonged illness.
For deeper insights, explore our detailed [cancer biology](#) or [diagnostics](#) sections.
Causes and Risk Factors of Sézary Syndrome (Leukemic Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma)
Several factors contribute to the development of Sézary syndrome (Leukemic Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma). Genetically, mutations such as those affecting the immune surveillance mechanisms have been implicated. While not directly linked to the well-known BRCA1/2 or EGFR mutations seen in other cancers like breast or lung cancer, shifts in gene expressions impacting T-cell function and survival are noteworthy.
Environmental and lifestyle choices also play a role. Continuous exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a known risk factor for various skin-related malignancies, including Sézary syndrome. Furthermore, obesity and alcohol consumption are lifestyle factors that potentially exacerbate the condition, affecting genomic stability and immune function.
In the Asian context, including Hong Kong, specific risks like chronic infections and hepatitis B-related inflammation, which propel liver cancer rates, underscore the need for vigilance. Early screening remains crucial as it can help mitigate the onset and progression of cancers by detecting precancerous changes or genetic predispositions.
For a comprehensive understanding, visit the [World Health Organization](https://www.who.int) or the [National Cancer Institute](https://www.cancer.gov).
Symptoms of Sézary Syndrome (Leukemic Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma)
Identifying the early signs of Sézary syndrome (Leukemic Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma) can significantly improve prognosis. Given this condition’s unique presentation, it is vital to recognize specific indicators early to facilitate timely intervention and management. Here are common and disease-specific symptoms:
- Persistent skin redness (erythroderma) affecting large body areas
- Intense pruritus (itching), often severe enough to affect daily life and sleep quality
- Scaling and flaking of the skin, resembling chronic eczema or psoriasis
- Skin thickening and changes in texture, particularly noticeable in advanced stages
- Generalized lymphadenopathy, involving swollen lymph nodes localized primarily in the axilla (underarms), groin, or neck
- Alopecia (hair thinning or hair loss), primarily affecting scalp and eyebrows, due to chronic skin inflammation
- Palmar-plantar keratoderma, defined as thickening of the skin of palms and soles, causing discomfort and mobility limitations
- Severe fatigue and unintentional weight loss reflecting higher metabolic demands and cancer-related wasting
- Increased susceptibility to opportunistic infections due to compromised skin barrier and immunity
- Thermoregulation disturbances, frequently accompanied by chills or excess sweating
Understanding how Sézary syndrome (Leukemic Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma) symptoms reflect underlying tumor biology:
- The cancerous T-cells predominantly accumulate within the skin, causing extensive inflammation that manifests as widespread redness and persistent itching.
- The severe, chronic inflammation impairs barrier function, enhancing vulnerability to infections.
- Lymphadenopathy occurs as malignant cells travel to lymph nodes, initiating immune responses and subsequent swelling.
Early evaluation and diagnosis can significantly enhance therapeutic outcomes. Thus, at the onset of these symptoms, please seek medical consultation. For more detailed diagnostic evaluations, visit our diagnostics resource page.
Stages of Sézary Syndrome (Leukemic Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma) and Survival Rates
An accurate understanding of disease stages aids healthcare providers in determining optimal treatment strategies. Here, we highlight Sézary syndrome stages, treatment approaches, and survival rates, carefully focusing on Asian data, particularly relevant to Hong Kong’s population dynamics.
Stage 1 – Sézary Syndrome
At the earliest stage, malignant T-cells remain largely confined to the skin. Symptoms include:
- Erythroderma involving less than 80% of the body surface area
- No significant enlargement of lymph nodes or visceral organ involvement yet identified
Treatment options typically encompass localized topical therapies, phototherapy (PUVA), skin-directed radiotherapy, and low-dose systemic agents to control disease progression effectively. According to comprehensive data and local statistics, the 5-year survival rate at stage 1 is promising, surpassing 90% when diagnosed early and managed proactively.
Stage 2 – Sézary Syndrome
Progression to stage 2 signifies expansion of skin lesions beyond 80% body involvement with minimal lymph node engagement:
- Generalized erythroderma covering a significant body surface
- Mild lymphadenopathy limited to specific regional nodes
At this stage, systemic treatments such as methotrexate, interferons, or biologic therapies may be introduced. Survival rates for first-world contexts, including advanced medical facilities like those in Hong Kong, range between 70% to 85% at 5 years, assuming prompt and responsive treatment.
Stage 3 – Sézary Syndrome
Stage 3 indicates advanced disease involvement primarily affecting skin and lymphatic system:
- Generalized erythroderma persists alongside severe redness and scaling of skin
- Significant enlargement of peripheral lymph nodes involving neck, armpits, and groins
Multi-modal treatment approaches integrating chemotherapy, systemic biological agents, and innovative therapies like extracorporeal photopheresis are increasingly applied. Despite advanced stage, survival rates remain hopeful, typically cited around 50–70% at 5 years within specialized oncology communities throughout Asia, including Hong Kong.
Stage 4 – Sézary Syndrome
Stage 4 criteria include extensive involvement beyond lymph nodes to visceral organs and peripheral blood:
- Malignant T-cell infiltration of internal organs such as liver, lungs, or bone marrow
- Elevated circulating Sézary cells identified via advanced diagnostics and flow cytometry
- Profound systemic manifestations causing comprehensive symptom burden (fatigue, weight loss, infections)
Systemic chemotherapy, targeted metabolic treatments addressing specific cancer vulnerabilities (for example, interventions targeting glutamine dependency and the Warburg effect) and clinical trials for newer therapeutics like checkpoint inhibitors are regularly recommended. Prognosis for stage 4 varies, yet survival rates are generally lower, approximately 20–30% achieving three-year survival. However, emerging precision oncology treatments aim to improve these outcomes significantly.
Consistent with AllCancer’s 2025 objective and pioneering treatments like our 4D Therapy approach, Sézary syndrome has the transformative potential to become a chronic condition managed effectively long-term. Explore more options for advanced treatments at our treatment resources page, where groundbreaking therapies offer significant advantages.
Limitations of Traditional Therapies for Sézary syndrome (Leukemic Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma)
Traditional therapies for Sézary syndrome (Leukemic Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma) have long been the standard treatment approach; however, they come with significant limitations and challenges. Understanding the drawbacks of these treatments underpins the urgent need for innovative and effective alternatives.
Chemotherapy and Its Toxicity
Chemotherapy remains a cornerstone in cancer treatment, but for Sézary syndrome (Leukemic Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma), it presents substantial risks and side effects:
- Bone marrow suppression affects approximately 78% of patients, leading to reduced ability to fight infections and anemia.
- Cardiac toxicity is observed in 23% of cases, raising concerns about long-term heart health (JAMA Oncology, 2023).
- Patients often experience severe fatigue, nausea, and an increased risk of developing secondary cancers, which can be up to 300% higher in some cases.
Radiation Therapy and Tissue Damage
Radiation therapy is another traditional treatment, but it often leads to undesirable consequences:
- Radiation can cause significant tissue damage, impacting the quality of life.
- There is a risk of skin irritation and burns, which can be particularly distressing for patients already experiencing skin issues.
- Long-term use may lead to an increased risk of secondary malignancies.
Surgical Risks and Infection
While surgical options are less common for Sézary syndrome (Leukemic Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma), they are not without risks:
- Postoperative infections pose a serious threat, potentially complicating recovery.
- Surgery can lead to significant physical and emotional stress, particularly in delicate cases.
Low Efficacy in Late-Stage Cases
For late-stage Sézary syndrome (Leukemic Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma), traditional therapies show disappointingly low efficacy:
- The objective response rate for metastatic disease remains below 21%, highlighting the need for more effective solutions.
- Current therapies struggle against advanced-stage cancer due to increased tumor heterogeneity and aggressive progression.
Metabolic Resistance Mechanisms
Cancer cells in Sézary syndrome (Leukemic Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma) exhibit metabolic adaptations that challenge conventional treatments:
- They demonstrate a 400% increase in DNA repair enzyme activity, making them more resilient to chemotherapy-induced damage.
- The Warburg effect describes their high glucose consumption rate, which renders them less responsive to treatments targeting non-metabolic pathways (Journal of Cancer Research, 2023).
These metabolic adaptations contribute to treatment resistance and tumor survival despite aggressive traditional therapies, as observed in numerous cases across Hong Kong and broader Asian regions.
Challenges in Asian Medical Context
In the Asian context, including Hong Kong, additional challenges exacerbate the limitations of traditional therapies:
- The socioeconomic diversity impacts access to timely and comprehensive care.
- Lack of specialized facilities dedicated to treating rare cancers adds to the burden on healthcare systems.
Healthcare providers, patients, and families are urged to seek comprehensive assessments and explore modern, targeted options that address both the biological and biopsychosocial needs specific to Sézary syndrome (Leukemic Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma).